What is a widget and what are plugins actually for? Why do I need a database? Which updates do I need to take care of and what exactly is a theme? I still remember the time when I didn’t understand the meaning of common WordPress terminology like widgets, plugins, or themes and all these foreign words used to cause me quite a headache. I wanted to use WordPress and create my first blog, but I did not have a clue what all that WordPress tech talk actually meant.
Since WordPress can be a little bit intimidating to beginners with all those specific terms, I prepared a little overview explaining the most important WordPress terms.
1. Frontend and Backend
If you start out with WordPress, it’s important to learn about the difference between the frontend and backend of your WordPress website.
The frontend is the part of the website that your visitors see, when they type in your URL into their web browsers. The backend, on the contrary, is the part of the WordPress site that only you can see and to which you have access by typing in your WordPress username and your password. In the backend (or admin area) you can manage your WordPress site, write new articles, create pages, install plugins and update your plugins, themes or WordPress itself.
2. The Dashboard
In WordPress the main page (or landing page) of the backend is called Dashboard. You can find the link to your Dashboard at the very top of your admin menu in your WordPress backend. You can customize your Dashboard and add or hide certain sections by clicking on the grey “Screen Options” button at the top right of your admin area.
3. Themes
Of course, at Elmastudio themes are our favorite topic. Themes are the design templates for WordPress websites. In other words, the theme is responsible for the look of the website in the frontend.
Each WordPress website needs to have a theme, therefore WordPress already comes with a default theme installed. You can change the default theme to a different one under Appearance → Themes. You can choose from one of the offered free themes that are available directly in your admin area under “Add New”. Also, you can install your own theme or a Premium theme, if you click the “Upload Theme” button.
Since WordPress is so flexible, there are themes available for a number of different purposes. You can choose a pure blog theme, a business theme, a theme for your online portfolio or magazine, or even for your own online shop.
4. The Blog
WordPress is mostly described as a blogging software, but what actually is a “blog”?
A blog is a form of online log book or journal that offers the possibility to create regular posts. In contrast to a static website that you create once and that rarely or never changes, a blog changes frequently by publishing new blog posts. A blog is therefore much more exciting to read and visit.
Not only are there hobby blogs, but also professional blogs and online magazines out there. Nowadays many companies also blog in order to communicate better with their customers. The possibility to post comments is another great feature of blogs. Readers are able to post their comments below each published article, which makes it possible to discuss the topic of your post together with your readers.
5. Posts vs. Pages
By default WordPress offers two different types of formats to publish content – posts and pages. Posts are great to create dynamic content on your website, they can be viewed on your blog ordered by their publish date.
Pages on the other hand are the static part of your WordPress site. You will mostly create the content of your pages once and not update the content often. Therefore you will use pages for information such as your About page or a Contact page. You can also update your pages as well to edit information and add new pages to your website. You can filter posts by categories or tags to better organize your blog content.
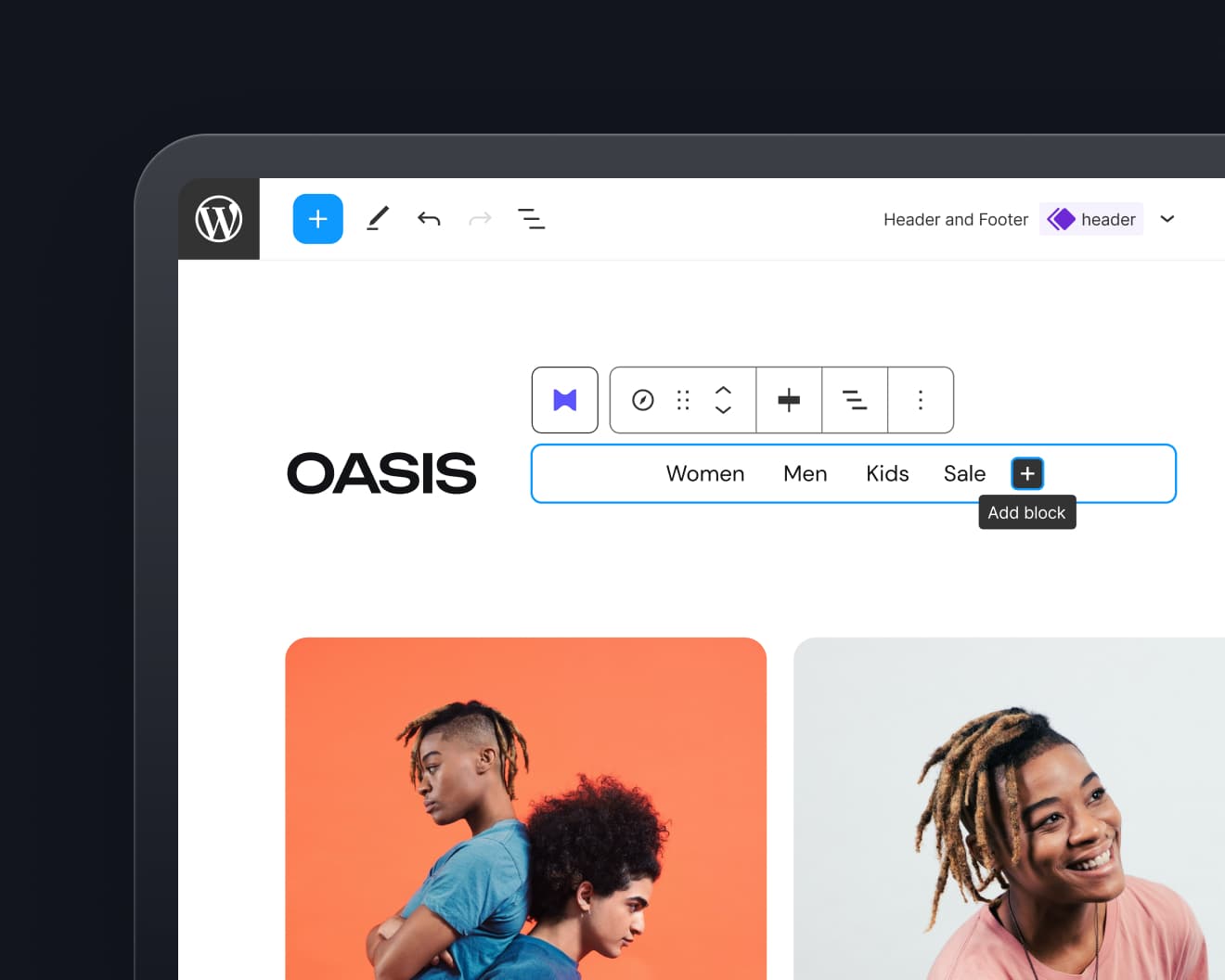
6. Widgets
Widgets offer the possibility to add small, additional sections to your website. In most cases, widgets will contain sub information about your website or blog, i.e. a list of your blog categories, a list of links to your social sites, a preview of your latest Instagram pictures and so on.
Widgets can be added to the widget areas of a theme under Appearance → Widgets. Here you can also find all default WordPress widgets. Often, themes or plugins will also offer additional custom widgets.
7. Sidebar
A sidebar is the small right or left aligned section of a website next to your main content area (containing your posts or pages). On WordPress sites, sidebars will mostly contain a widget area so that you can add additional information about your blog in the sidebar section.
8. Plugins
Plugins are another important part of WordPress. With the use of plugins, you can add endless additional features to WordPress that go way beyond the WordPress core features. You can find a list of all free WordPress plugins (that were tested and approved by the WordPress.org team) in the WordPress.org Plugin directory.
With plugins, it’s possible to add small features to your website like social media buttons to share your posts. You can also use plugins to create an entire online shop with WordPress, make your WordPress site multilingual, add spam filters for your comments, optimize your website security and much more. By using plugins, WordPress becomes so much more flexible, as they offer thousands of interesting opportunities to create your own website with WordPress.
An important note is that you can only use plugins with a self-hosted WordPress site. It is not possible to install plugins on WordPress.com hosted websites.
9. Database
All information on your WordPress site (your post and page content, comments, links, users, passwords…) is stored in a database. If you want to set up a WordPress website for the first time it is important that you choose a website hosting package that includes a MySQL database.
Since all this valuable information is stored in your database, it’s important that you backup your database on a regular basis. This way you can always use the latest database backup, should you loose your data. Luckily, there are a number of helpful WordPress plugins available to help you with your database backups (e.g. WP-DBManager or VaultPress).
10. Updates
Next to backups of your WordPress site and database, it is also important that you keep all your themes, plugins, and WordPress itself up-to-date. Therefore, it’s important to follow the update instructions in your dashboard and make sure that all themes, plugins, and WordPress runs on the latest version.
Your Feedback
Do you have questions or suggestions for additional terms that I should explain here in the post? Which WordPress-specific terms do you find most important to understand?
I would love to hear your questions, feedback and further suggestions in the comments below!

Leave a Reply